Search-Query Documentation





Search Query is a Python package designed to load, lint, translate, save, improve, and automate academic literature search queries. It is extensible and currently supports PubMed, EBSCOHost, and Web of Science. The package can be used programmatically, through the command line, or as a pre-commit hook. It has zero dependencies and integrates in a variety of environments. The parsers and linters are battle-tested on peer-reviewed searchRxiv queries.
Installation
To install search-query, run:
pip install search-query
Quickstart
Creating a query programmatically is simple:
from search_query import OrQuery, AndQuery
# Typical building-blocks approach
digital_synonyms = OrQuery(["digital", "virtual", "online"], field="abstract")
work_synonyms = OrQuery(["work", "labor", "service"], field="abstract")
query = AndQuery([digital_synonyms, work_synonyms])
A query can also be parsed from a string or a JSON search file (see the overview of platform identifiers):
from search_query.parser import parse
query_string = '("digital health"[Title/Abstract]) AND ("privacy"[Title/Abstract])'
query = parse(query_string, platform="pubmed")
The built-in linter functionality validates queries by identifying syntactical errors:
from search_query.parser import parse
query_string = '("digital health"[Title/Abstract]) AND ("privacy"[Title/Abstract]'
query = parse(query_string, platform="pubmed")
# Output:
# ❌ Fatal: unbalanced-parentheses (PARSE_0002)
# - Unbalanced opening parenthesis
# Query: ("digital health"[Title/Abstract]) AND ("privacy"[Title/Abstract]
# ^^^
Once a query object is created, it can be translated for different databases.
The translation illustrates how the search for Title/Abstract is split into two elements:
1from search_query.parser import parse
2
3query_string = '("digital health"[Title/Abstract]) AND ("privacy"[Title/Abstract])'
4pubmed_query = parse(query_string, platform="pubmed")
5wos_query = pubmed_query.translate(target_syntax="wos")
6print(wos_query.to_string())
7# Output:
8# (AB="digital health" OR TI="digital health") AND (AB="privacy" OR TI="privacy")
The translated query can be saved as follows:
1from search_query import SearchFile
2
3search_file = SearchFile(
4 query=wos_query,
5 authors=[{"name": "Tom Brady"}],
6 record_info={},
7 date={}
8)
9
10search_file.save("search-file.json")
Demo
A Jupyter Notebook demo (hosted on Binder) is available here:
Try the interactive web GUI in your browser: search-query-gui.
Functional overview
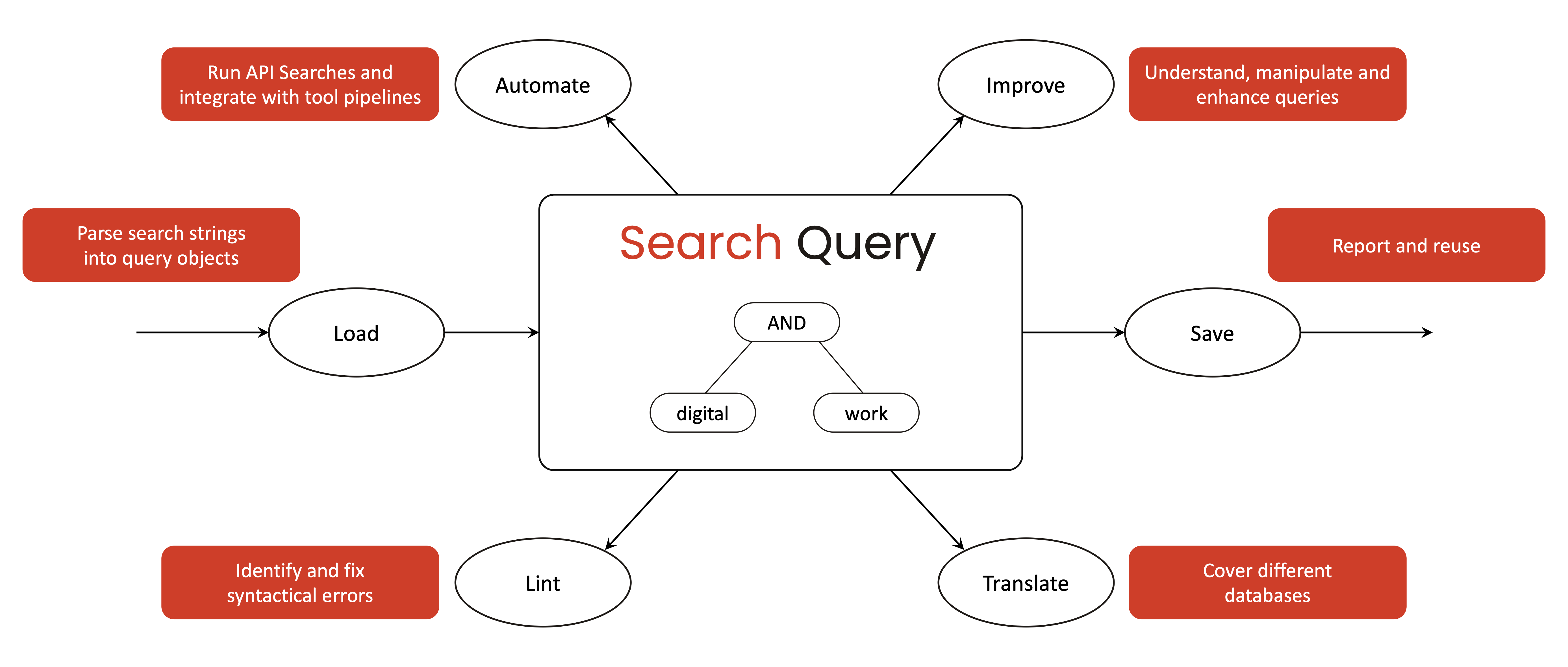
search-query treats academic search strategies as structured query objects rather than static strings. Query objects can be created programmatically or derived from search strings or JSON files, and are represented as object-oriented structures that capture Boolean logic, nesting, and field restrictions. Based on a query object, search-query supports the following operations:
Load: search-query provides parsing capabilities to ingest search queries from both raw strings and JSON files. It parses database-specific query strings into internal, object-oriented representations of the search strategy. This allows the tool to capture complex Boolean logic and field restrictions in a standardized form.
Save: Researchers can serialize the query object back into a standard string or file format for reporting and reuse. This facilitates transparency and reproducibility by allowing search strategies to be easily reported, shared or deposited.
Lint: search-query can apply linters to detect syntactical errors or inconsistencies that might compromise the search. It can check for issues such as unbalanced parentheses, logical operator misuse, or database-specific syntax errors.
Translate: The library can convert a query from one database syntax into another, enabling cross-platform use of search strategies. Using a generic query object as an intermediate representation, search-query currently supports translations between Web of Science, PubMed, and EBSCOHost.
Improve: Beyond basic syntax checking and translation, search-query aims to support query improvement to enhance recall and precision. As queries are represented as manipulable objects, researchers can programmatically experiment with modifications — for example, adding synonyms or adjusting field scopes — to observe how these changes affect the search results.
Automate: Automation primarily refers to the integration with systematic review management systems, such as CoLRev. The library offers programmatic access via its Python API, which means it can be embedded in scripts and pipelines to run searches automatically. It also provides a command-line interface and git pre-commit hooks, allowing researchers to incorporate query validation into version control and continuous integration setups.